Providing Effective Solutions Of Utilizing Water For Customers
Asynchronous Motor Manufacturers
-

YL Single Phase Two-value Capacitor Asynchronous Motor
The housing, front and back cover are made of cast-iron,with high hardness, strong bearing capacity, firm structure and ... -

YE3 High Efficiency Three-phase Asynchronous Motor
YE3 series is a fully enclosed fan-cooled squirrel cage type high efficiency three-phase asynchronous motor newly develo... -

YE2 High Efficiency Three Phase Asynchronous Motor
YE2 electric motor has options of both aluminum housing and cast iron housing. Cast iron housing electric motor comes wi... -

Y2 High Efficiency Three Phase Asynchronous Motor
The housing, front and back cover are made of cast-iron,with high hardness, strong bearing capacity, firm structure and ... -

MS High Efficiency Three Phase Asynchronous Motor
Aluminum housing,aluminum front and back cover,aluminum terminal box,aluminum feet which is removable.The installation p... -

MF High Efficiency Three Phase Asynchronous Motor
Aluminum housing,aluminum front and back cover,aluminum terminal box,aluminum feet which is removable.The installation p...
Start Our Cooperation!
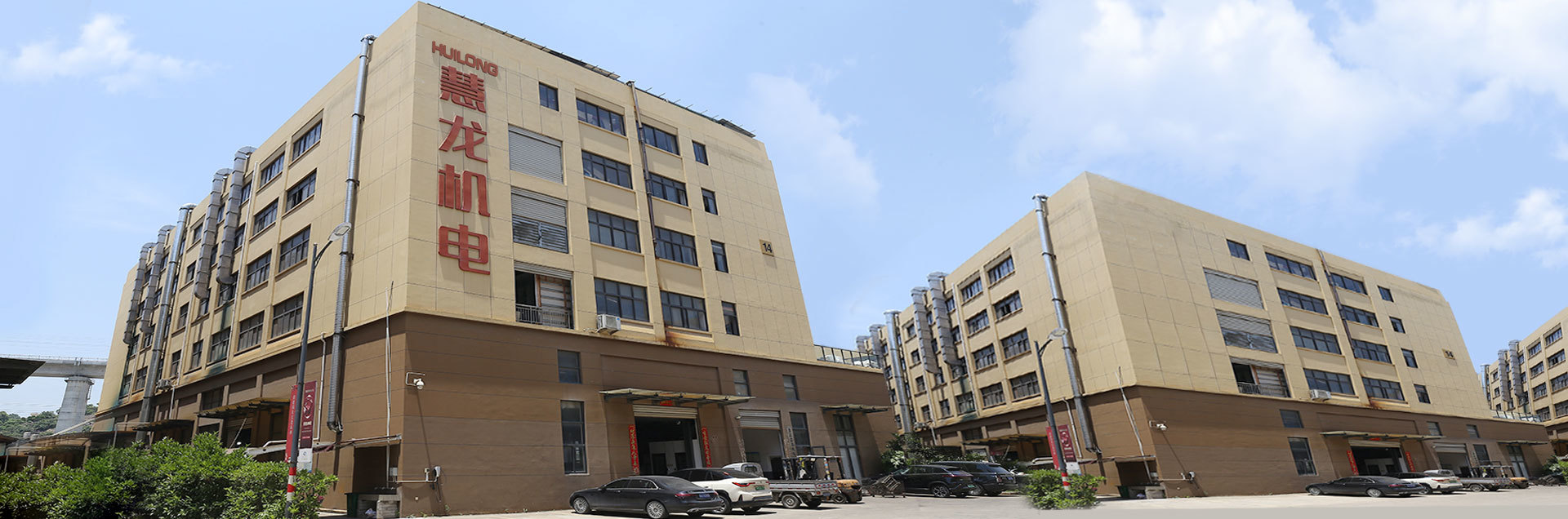

Zhejiang Huilong Electromechanical Co., Ltd. was established in 2007. The company covers an area of 6000m² and has more than 200 employees. It is an industry-trade enterprise specializing in the production of water pumps. It can produce more than 30,000 pumps of various types, mainly exported to Europe, Asia, Africa, America, and other regions.
The company has rich experience in the design and manufacture of submersible pumps and sewage pumps, advanced automated production lines, testing equipment, and production processes, a group of professional technical engineers, and a strong R&D team. Since the establishment of the company, the products have been produced in strict accordance with international standards. Every position in production, sales, and after-sales has a superb technical team to back it up. Every link is under strict quality control to ensure that all sales are high-quality products. The employees of the company always keep in mind that quality is the life of an enterprise, and they are professional because of concentration, and we have been working hard.
-

Products Integration
-
15+ Industrial Experience
-

Export To Over 35 Countries
-

7*24 Hours Customer Service
Recent News
Industry Knowledge
-
pending upgrade
-
pending upgrade


 中文简体
中文简体 عربى
عربى